Yeast is a form of fungus that can cause an infection known as a yeast infection. This is found throughout the body.
Candidiasis is the most common type of yeast infection. There are around 20 species of Candida, with Candida albicans being the most prevalent.
Infections occur when a large number of fungi congregate in one region due to favorable environmental circumstances. These disorders are prevalent in warm, moist parts of the body. Typical examples include the following:
Vaginal yeast infections, infections under the armpits, thrush (tissue infections in the mouth and throat), skin and diaper rash, and nail bed infections are also common.
Under normal conditions, your skin efficiently blocks the yeast, but if you have any cuts or gaps in your skin, the likelihood of the organism entering those regions increases.
The mouth and diaper areas are the most often affected areas in infants.
Candidiasis vaginalis, or vaginal yeast infection, is the most common type of vaginitis.
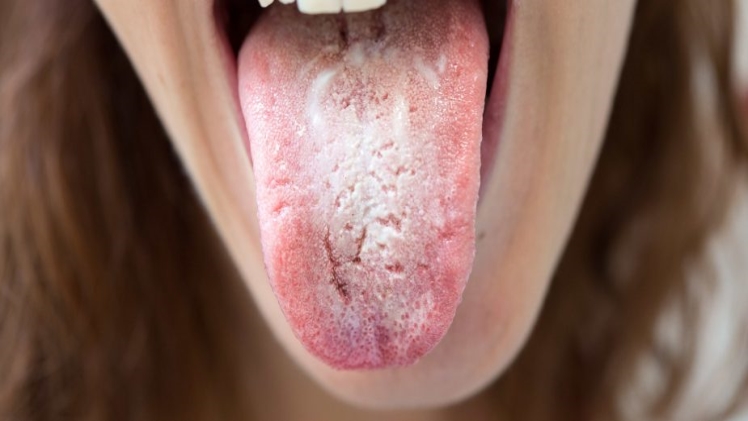
Adults are more likely to develop oral yeast infections as they age. Yeast infections can also occur around dentures, in skin folds (most commonly beneath the breast and lower belly), and in nail beds. Treatment of these types of candida infections may be quite effective, but infections in the nail beds typically require prolonged therapy.
A yeast infection seldom spreads across the body. Up to 45% of patients with systematic candida disease (in which the fungus enters the circulation and spreads throughout the body) die.
Even common oral and vaginal yeast infections can progress to serious illness and are typically more resistant to standard therapy.
Recurrence of certain yeast infections may serve as a warning sign of more serious conditions, such as diabetes, leukemia, or AIDS.
Candida Factors
Candidiasis Yeast Infection Causes:
In women, yeast infections are the second most frequently occurring cause of vaginal burning, itching, and discharge. Yeasts have been found in the vagina of 20% to 50% of healthy women. These yeasts have the potential to overgrow if the environment within the vagina changes. The most prevalent cause of yeast overgrowth is the use of antibiotics or steroids. Yeast infections can also be caused by pregnancy, menstruation, sperm, diabetes, and birth control drugs. After menopause, the risk of yeast infections significantly increases.
In rare situations, individuals have a compromised immune system as a result of cancer therapy, steroid usage, or infectious infections such as HIV/AIDS. Candidal infections can spread throughout the body in such instances, posing a life-threatening threat. Candida most frequently attacks the blood, brain, eyes, kidney system, and heart. Candida can also infect the lungs, liver, and spleen. AIDS patients frequently develop esophagitis, an inflammation of the swallowing tube. Candida is a major contributor to this.
Around 15% of those with compromised immune systems suffer from chronic infections caused by Candida. This is because a weaker immune system makes it easier for pathogens to enter the circulation via skin cuts.
When antibiotics are taken frequently, they can eliminate the beneficial bacteria that fight yeast infections, resulting in a buildup of Candidal organisms in a particular region, resulting in infection.
Candida Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of a candida infection vary according on the location of the infection.
Female vaginal yeast infection:
To diagnose a vaginal yeast infection, doctors look for a thick white discharge that resembles cottage cheese.
Typically, the infection causes itching or irritation in the vaginal region and adjacent outer tissues. In certain circumstances, pain during sexual intercourse or burning when urinating may occur.
Male genital yeast infection:
Men who have interacted with a woman who has a vaginal yeast infection are more likely to get genital yeast infection symptoms. Yeast is naturally present in a woman’s body and cannot be transmitted from another source. As a result, a yeast infection is not considered a sexually transmitted infection (STD).
Treatment is not indicated until a woman’s male sex partner shows signs of candida yeast infection. The most common symptoms are itching and burning sensations in the penis, as well as a rash on the penile skin.
Other common fungal infections common in males include Jock-Itch and athlete’s foot prevalent among athletes. These can be easily treated at home using natural topical ointments for fungal infections.